Exploring Educational Attainment Across U.S. Cities: Insights and Implications
Top U.S. Cities Excelling in Education: What Drives Their Success?
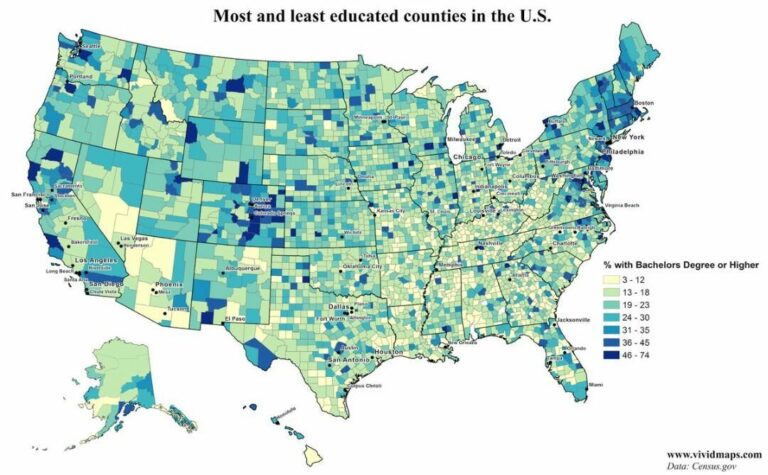
Across the United States, certain metropolitan areas have emerged as leaders in educational achievement, propelled by dynamic economies and strategic educational investments. Boston, Massachusetts, for example, boasts a highly educated populace, largely due to its dense network of world-renowned universities and a booming life sciences and technology sector. Likewise, San Francisco, California, benefits immensely from its proximity to Silicon Valley, where advanced degrees are often essential for employment in cutting-edge industries.
Other cities such as Washington D.C. and Seattle, Washington also rank highly, supported by strong public education systems and access to prominent research institutions. These urban centers distinguish themselves through innovative educational programs that integrate traditional academics with emerging skill sets, fostering inclusivity and adaptability. Key contributors to their educational excellence include:
- Robust funding for higher education and lifelong learning initiatives
- Collaborative partnerships between academic institutions and local industries
- Efficient public transit systems enhancing campus accessibility
- Policies aimed at alleviating student debt and promoting degree completion
Educational Challenges in Lower-Ranked Cities and Their Economic Consequences
Cities with lower levels of educational attainment often grapple with intertwined socioeconomic issues that hinder sustainable growth. Limited access to well-paying jobs restricts household incomes, perpetuating cycles of poverty and economic inequality. These communities frequently face diminished consumer spending, increased strain on municipal budgets, and challenges in maintaining essential public services such as healthcare and infrastructure.
Moreover, a less educated workforce can dampen productivity and innovation, making it difficult for these cities to attract and retain businesses that drive economic vitality. The broader repercussions include:
- Elevated unemployment rates due to skill shortages
- Higher healthcare costs linked to reduced preventive care awareness
- Increased crime rates stemming from limited opportunities and social disenfranchisement
- Brain drain as skilled individuals migrate to more educated urban hubs
| Area of Impact | Economic Effect |
|---|---|
| Workforce Competency | Slower innovation and reduced business expansion |
| Household Earnings | Lower tax revenues, limiting public investment |
| Community Health | Increased public healthcare spending |
| Social Cohesion | Heightened crime and safety challenges |
Effective Approaches to Elevate Education in Struggling Urban Areas
Improving educational outcomes in cities facing academic underperformance requires comprehensive strategies that extend beyond conventional classroom instruction. Community-driven initiatives, personalized tutoring programs, and mentorship opportunities tailored to local needs have demonstrated measurable success. Equipping schools with modern technology and updated learning resources is essential to bridge the educational divide and empower students to compete on equal footing with peers from more affluent regions.
Key strategies proven to enhance academic achievement include:
- Incorporating culturally responsive teaching materials that resonate with diverse student populations
- Expanding access to early childhood education to address achievement gaps from the outset
- Offering incentives to attract and retain skilled educators
- Fostering strong family and community partnerships to support student success
- Utilizing data analytics to customize interventions and track progress effectively
| Intervention | Outcome | Illustrative City |
|---|---|---|
| After-School Academic Support | Raises standardized test scores by approximately 15% | Cleveland |
| Culturally Relevant Education | Enhances student engagement by 20% | New Orleans |
| Teacher Retention Incentives | Decreases turnover rates by 25% | Memphis |
Bridging the Education Divide: The Role of Businesses and Policymakers in Workforce Development
Closing the educational gap necessitates concerted efforts from both the private sector and government leaders, focusing on upskilling current employees and broadening access to quality education. Corporations can collaborate with educational institutions and vocational centers to establish apprenticeship and internship programs that provide hands-on experience. By investing in continuous professional development and offering financial support for further education, businesses cultivate a motivated workforce equipped to meet evolving industry demands.
Meanwhile, policymakers are instrumental in creating equitable opportunities by increasing funding for STEM education, enhancing public transit to improve access to learning facilities, and incentivizing local hiring and training initiatives. Combining tax benefits for workforce development with support for community-based educational programs can significantly reduce disparities. The table below outlines key investment areas and their anticipated benefits:
| Investment Area | Target Groups | Projected Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Apprenticeship and Internship Programs | Young adults, career changers | Increased employment rates |
| STEM Education Funding | Students in underserved communities | Enhanced technological proficiency |
| Tax Incentives for Training | Small and medium-sized enterprises | Expanded employee development initiatives |
| Community Education Grants | Local nonprofits and schools | Improved adult education opportunities |
Conclusion: Navigating Educational Disparities for a Stronger Future
The educational attainment landscape across American cities reveals stark contrasts that mirror broader socioeconomic patterns. CNBC’s recent ranking of the most and least educated cities underscores how factors such as economic vitality, institutional access, and community investment shape educational outcomes. For policymakers, educators, and business leaders, recognizing these regional differences is vital to crafting strategies that promote equitable education and sustainable economic growth. Addressing the challenges faced by cities with lower educational levels will be essential to building a more inclusive, competitive, and prosperous national workforce.