California Academy of Sciences: A Trailblazer in Eco-Conscious Architectural Innovation
The California Academy of Sciences has once again pushed the envelope in sustainable architecture through a visionary partnership between Renzo Piano Building Workshop and Stantec Architecture. This transformative project, recently highlighted on ArchDaily, exemplifies a harmonious blend of avant-garde design, environmental mindfulness, and educational engagement. Situated prominently in San Francisco’s cultural scene, the Academy’s renovation not only enriches visitor interaction but also pioneers new benchmarks for eco-friendly construction globally.
Revolutionizing Sustainable Architecture at the California Academy of Sciences
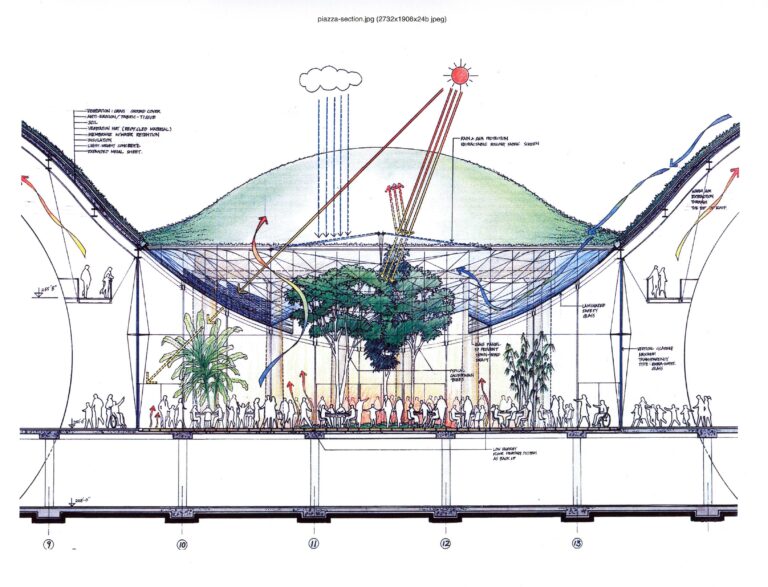
Marrying cutting-edge innovation with a deep commitment to environmental preservation, the California Academy of Sciences has set a new paradigm for sustainable building design. The collaboration between Renzo Piano Building Workshop and Stantec Architecture manifests in a structure that champions ecological responsibility through advanced green technologies and nature-inspired design concepts. The building‚Äôs signature feature‚ÄĒa sweeping living roof planted with indigenous Californian flora‚ÄĒmitigates urban heat effects while fostering local wildlife habitats, embodying a regenerative architectural philosophy.
Beyond the iconic rooftop, the facility incorporates several eco-conscious systems, including:
- Photovoltaic solar arrays that generate nearly 50% of the building’s electricity needs.
- Innovative water recovery mechanisms that halve the consumption of potable water.
- Natural airflow designs that significantly reduce reliance on mechanical cooling systems.
| Feature | Environmental Impact | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Living Roof | Decreases heat absorption | Enhances urban biodiversity |
| Solar Panels | Achieves 40-50% energy autonomy | Minimizes carbon emissions |
| Water Reclamation | Reduces potable water use by 50% | Conserves regional water supplies |
Cutting-Edge Architectural Approaches by Renzo Piano and Stantec
The joint effort of Renzo Piano Building Workshop and Stantec Architecture has yielded a landmark that reimagines sustainability and visitor engagement through innovative design. The building’s undulating green roof is not only an aesthetic marvel but also functions as a living ecosystem, capturing rainwater and lowering energy consumption. This biomimicry-driven design pushes the envelope on how architecture can symbiotically integrate with natural environments.
Highlighted design innovations include:
- Optimized daylighting: Utilization of state-of-the-art glazing technology to maximize natural illumination while curbing heat influx.
- Enhanced natural ventilation: Incorporation of operable windows and strategically positioned vents to promote airflow and reduce mechanical cooling.
- Eco-friendly materials: Preference for recycled and locally sourced components to minimize environmental impact.
- Versatile interior layouts: Adaptable spaces designed to accommodate diverse exhibits and evolving scientific narratives.
| Design Feature | Benefit | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Green Roof | Manages stormwater runoff | Enhances groundwater replenishment |
| High-Performance Glazing | Boosts energy efficiency | Reduces HVAC energy demand by 30% |
| Flexible Interiors | Supports multifunctional use | Improves visitor engagement and experience |
Blending Natural Elements and Technology to Elevate Visitor Engagement
The California Academy of Sciences elevates visitor interaction by seamlessly merging advanced technology with the verdant natural environment surrounding the building. The living roof doubles as an ecological asset and an interactive educational tool. Embedded sensors track microclimatic variations across the diverse plant species, relaying live data to digital kiosks inside the museum. This real-time environmental monitoring fosters an immersive learning environment where science and sustainability intersect.
Complementing the living roof, augmented reality (AR) guides throughout the museum enrich the visitor experience by layering additional context onto exhibits. Through handheld devices or mobile applications, guests can explore complex ecological concepts or visualize evolutionary histories superimposed on actual specimens. This tech-forward approach is supported by:
- Solar-powered adaptive lighting that adjusts brightness based on natural sunlight, optimizing energy use.
- Interactive digital displays offering in-depth information on local flora and fauna.
- Automated climate control systems that maintain ideal conditions for living exhibits and visitor comfort.
| Feature | Natural Integration | Technological Component |
|---|---|---|
| Living Roof | Supports native pollinators and plant species | Microclimate sensors feeding data to visitor kiosks |
| Exhibit Interaction | Displays real habitats and specimens | AR applications enhancing educational depth |
| Energy Management | Maximizes natural daylight | Solar-powered, adaptive lighting systems |
Guidelines for Future Sustainable Cultural Venues
To advance sustainability in upcoming cultural institutions, architects and planners should emphasize the use of innovative, low-carbon materials that do not sacrifice longevity. Expanding renewable energy sources‚ÄĒsuch as solar, geothermal, and wind power‚ÄĒwill ensure a steady, eco-friendly energy supply. Buildings should be designed to respond dynamically to environmental changes, incorporating smart climate control and green roofs that boost biodiversity while lowering operational expenses.
Equally vital is fostering community involvement through educational initiatives focused on environmental responsibility. Future designs should include adaptable spaces that evolve with shifting cultural and sustainability demands, promoting inclusivity and awareness. Essential strategies encompass:
- Modular and adaptable architecture to facilitate long-term use and easy modernization.
- Utilization of recycled and regionally sourced materials to reduce ecological disturbance.
- Incorporation of living walls and natural ventilation to enhance indoor air quality.
- Water recycling systems tailored for diverse climates, from arid to temperate.
| Feature | Benefit | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Glass | Controls interior temperature, lowering HVAC energy use | Dynamic tinting window panels |
| Rainwater Harvesting | Reduces reliance on potable water | On-site cistern storage systems |
| Native Landscaping | Supports local ecosystems and reduces maintenance | Drought-tolerant plant species |
Final Thoughts
The partnership between Renzo Piano Building Workshop and Stantec Architecture in revitalizing the California Academy of Sciences exemplifies how innovative design can coexist with environmental stewardship. This project not only reimagines the potential of sustainable architecture but also highlights the influential role cultural institutions play in promoting ecological consciousness. As the Academy continues to captivate visitors with its state-of-the-art features and immersive experiences, it stands as a beacon for how thoughtful architecture can contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.