Mapping the Concentration of Fortune 500 Headquarters Across U.S. States
The geographic distribution of Fortune 500 company headquarters across the United States provides a compelling lens through which to view regional economic strength and corporate influence. This analysis delves into the states that host the largest clusters of these top-tier corporations, spotlighting the pivotal business centers that shape both domestic and international markets. From long-established industrial powerhouses to burgeoning innovation hubs, these states play a critical role in steering the American economy and impacting global trade and technological advancement. Join us as we uncover which states lead the Fortune 500 rankings and explore the implications for their economic vitality and future prospects.
Top States Hosting the Most Fortune 500 Headquarters
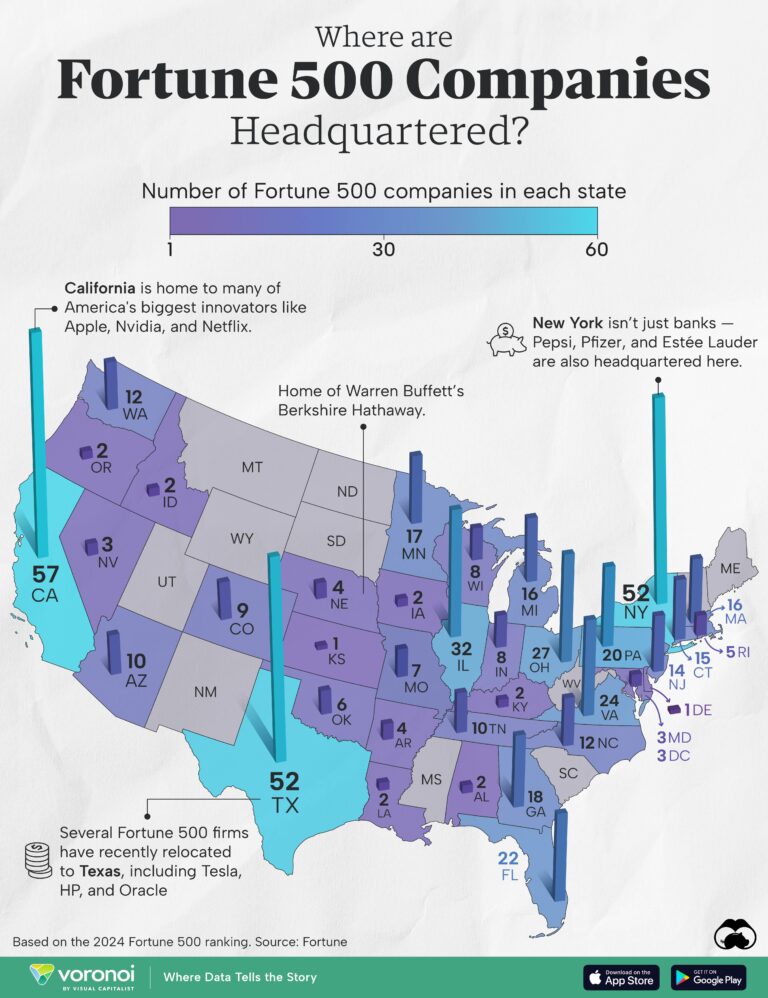
Several states stand out as dominant bases for Fortune 500 company headquarters, exerting significant influence over the national economic landscape. Leading the pack, New York continues to be a magnet for major corporations spanning finance, media, and technology sectors. Trailing closely are California and Texas, both of which boast thriving technology ecosystems, energy industries, and extensive multinational operations that bolster local economies and job markets.
These states share common attributes that foster corporate growth, including:
- Advanced infrastructure and efficient transportation systems
- Access to highly skilled talent pools from renowned universities
- Business-friendly regulatory frameworks
- Strategic locations facilitating domestic and international connectivity
| State | Number of Fortune 500 Headquarters | Leading Industries |
|---|---|---|
| New York | 47 | Finance, Media, Retail |
| California | 44 | Technology, Entertainment, Healthcare |
| Texas | 28 | Energy, Technology, Manufacturing |
| Illinois | 21 | Manufacturing, Finance, Consumer Goods |
How Fortune 500 Clusters Shape Local Economies
The aggregation of Fortune 500 companies within select states has transformed local economies by driving substantial job growth and infrastructure improvements. These corporate headquarters act as economic anchors, fostering ecosystems that include suppliers, service firms, and startups. The resulting employment opportunities elevate household incomes, while increased corporate tax revenues empower state and local governments to invest in public amenities such as education, transit, and safety services.
Nonetheless, this concentration also presents challenges. Rising real estate costs and widening income disparities can place pressure on community resources and exacerbate socio-economic divides. Localities must carefully balance the benefits of corporate presence with the need to maintain affordable housing and support small businesses. Below is an overview of typical economic effects linked to Fortune 500 company concentrations:
| Economic Factor | Positive Effects | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Employment | Growth in high-skilled job opportunities | Wage disparity and job polarization |
| Infrastructure | Enhanced transportation and utilities | Increased traffic congestion |
| Housing Market | Appreciation in property values | Escalating housing affordability issues |
| Local Enterprises | New partnerships and expanded client bases | Competition from large corporate chains |
Industries Powering Fortune 500 Growth in Leading States
The economic momentum behind states with the highest number of Fortune 500 headquarters is largely driven by several key sectors. In California and Texas, the technology and energy industries dominate, mirroring global trends toward innovation and sustainable energy solutions. Financial centers like New York and Illinois continue to thrive on banking, insurance, and investment services, which form the backbone of their corporate landscapes. These industries not only generate extensive employment but also stimulate related markets such as real estate, professional services, and logistics.
Additionally, healthcare and consumer goods sectors are vital contributors in states with expanding Fortune 500 presence. For instance, Massachusetts and Minnesota have become leaders in biotechnology and pharmaceuticals, advancing both scientific research and commercial distribution. Meanwhile, consumer product companies based in Georgia and Ohio are growing through retail and food manufacturing. The table below summarizes dominant industries in select top states:
| State | Primary Industry | Sector Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| California | Technology | Software Development, Semiconductor Manufacturing |
| Texas | Energy | Oil & Gas, Renewable Energy |
| New York | Finance | Banking, Asset Management |
| Massachusetts | Healthcare | Biotechnology, Medical Devices |
- Technology hubs continue to thrive in CaliforniaŌĆÖs Silicon Valley and Austin, Texas, driving innovation and startup growth.
- Financial services remain central to New York and Illinois, reinforcing their status as national finance leaders.
- Healthcare innovation strengthens MassachusettsŌĆÖ role as a biotech and pharmaceutical powerhouse.
- Energy sector diversification accelerates TexasŌĆÖ leadership in both traditional fossil fuels and renewable energy sources.
Effective Approaches to Attract Fortune 500 Firms in Emerging Regions
Enhancing Infrastructure and Ensuring Regulatory Clarity: Fortune 500 companies favor locations where operational efficiency is supported by dependable infrastructure and transparent regulations. Emerging markets can draw these corporations by investing in modern transportation, communication systems, and streamlined administrative procedures. Establishing clear, supportive legal frameworks reduces business risks and fosters confidence. Governments may also create special economic zones with customized incentives tailored to large multinational enterprises, encouraging sustained investment.
Developing Skilled Talent Pools and Innovation Networks: Access to a well-educated, adaptable workforce is a crucial factor for global corporations. Emerging markets with strong universities and vocational training programs position themselves as fertile grounds for innovation and expansion. Fortune 500 companies often seek collaborations with local startups and research institutions to harness new ideas while broadening their market presence. Public-private partnerships that nurture these ecosystems provide a competitive advantage and signal a business-friendly environment.
- Investment in digital and physical infrastructure
- Creation of tax-advantaged economic zones
- Emphasis on STEM education and workforce development
- Promotion of academia-industry collaboration
- Regulatory reforms to simplify business operations
| Strategy | Focus Area | Illustrative Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure upgrades | Operational efficiency | Minimized supply chain disruptions |
| Tax incentive zones | Cost competitiveness | Attraction of regional corporate offices |
| STEM education funding | Talent development | Enhanced innovation capabilities |
Final Thoughts
As the U.S. business environment continues to evolve, the concentration of Fortune 500 companies in select states highlights the dynamic economic forces shaping the nation. These states not only act as epicenters of corporate influence but also serve as engines of innovation, employment, and growth on a national scale. Monitoring the trends and shifts within these Fortune 500 strongholds offers valuable insights into the future trajectory of the American economy, revealing emerging opportunities and potential challenges in the years ahead.